Constructive feedback is essential for growth and development, both personally and professionally. The 4G feedback model provides a structured approach to giving and receiving valuable feedback. In this article, we dive deeper into this model and discover how it can contribute to more effective communication and performance improvement, with a focus on the psychology behind feedback.
The importance of constructive feedback
Effective feedback is an essential part of personal growth and professional development. It enables individuals and teams to leverage strengths and address weaknesses. Constructive feedback helps improve performance, increase engagement and create a positive work environment.
Use Learned’s FREE sample template to refresh and improve your feedback conversation. In fact, the start, stop & continue conversation is a modern alternative to a development review conversation. This switch will result in a feedback culture.
What does the 4G feedback model entail?
The 4G feedback model is a structured approach to giving and receiving feedback. The model consists of four essential elements: data, feelings, behavior and desired outcome. Here is a brief explanation of each element:
-
- Data: objective facts and observations about the person’s behavior.
- Feelings: the emotions or reactions that the behavior has evoked in the feedback giver.
- Behavior: description of observed behavior, including examples.
- Desired outcome: clear expectations and suggestions for improvement.
Roadmap: how to use the 4G feedback model.
Applying the 4G feedback model is simple and effective:
Step 1: Collecting data
Start by collecting objective data about the behavior you want to discuss. Be specific and use concrete examples.
Step 2: Expressing feelings
eel your feelings and emotions about the observed behavior in a respectful manner. Focus on how the behavior affected you.
Step 3: Describe the behavior
Give a detailed description of the behavior you observed. Be specific and avoid generalizations.
Step 4: Desired outcome and suggestions
Conclude by making clear what you expect from the person and what suggestions you have for improvement. Be positive and constructive.
Advantages of the 4G feedback model
The 4G feedback model offers several advantages:
-
- It promotes open communication and transparency.
- It reduces defensive reactions and conflicts.
- It provides a clear focus on behavior and improvement.
- It facilitates growth and development on a personal and professional level.
Practical tips for effective feedback with the 4G model
-
- Be empathetic and respectful when expressing feelings.
- Give feedback regularly, not just during formal reviews.
- Encourage open dialogue and be open to counter-feedback.
- Provides support and resources to encourage improvement, taking into account the psychology of behavior change.
Integrate a feedback culture with Learned
Create a feedback culture and encourage managers and employees to exchange compliments and feedback throughout the year. Use real-time feedback for examples in your assessment. Discover today how Learned can support you in achieving your feedback goals.
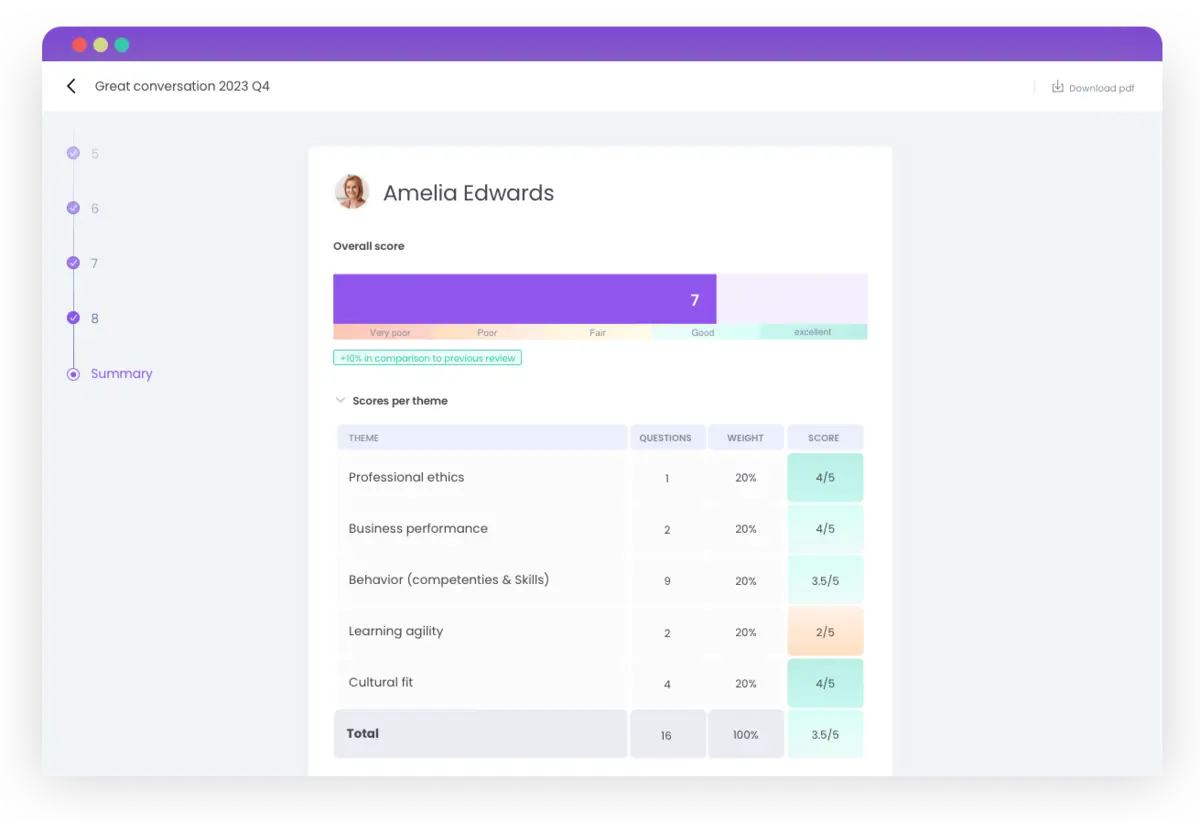
Learned facilitates objective evaluations. By creating multiple moments of measurement per year based on different themes – for example: the fit with your culture and goal achievement, you will gain objective insight into your low- and high performers. Explanation illustration: Each evaluation shows how the employee scores on the various themes.